A Practical Guide
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are no longer niche; they are driving innovation across all industries.
Behind the scenes, GPUs handle the heavy processing that enables these workloads. However, GPUs are expensive, sometimes scarce, and not always easy to manage at scale.
This is where Kubernetes comes in.
Originally developed by Google, Kubernetes is an open-source platform that automates the deployment, scaling, and management of containerised applications.
Containers are lightweight, portable execution environments that package code and dependencies.
Kubernetes orchestrates these containers across nodes, managing load, availability, and resources including GPUs. For more information about Kubernetes visit the link Kubernetes
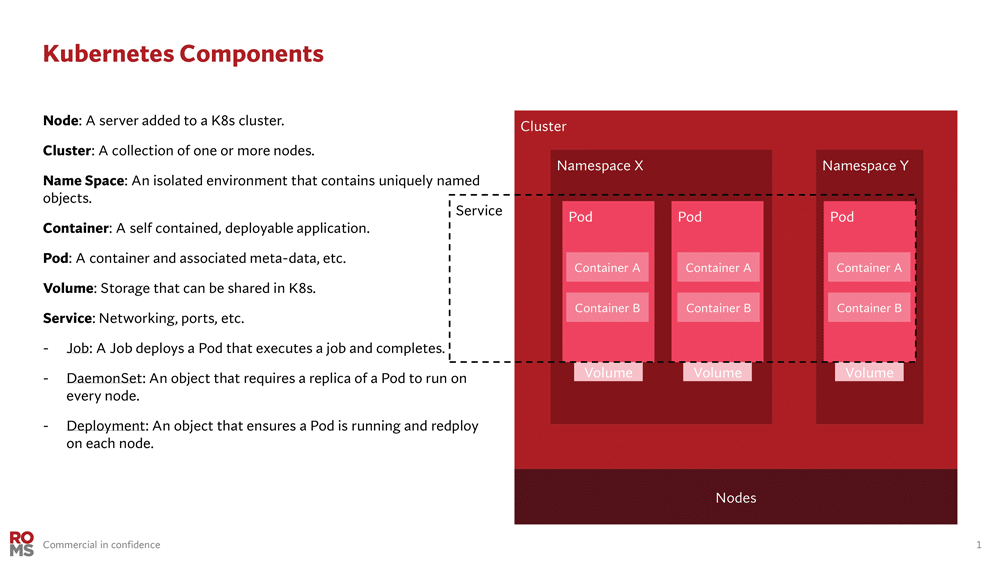
Kubernetes has rapidly become the platform of choice for distributing AI workloads.
It offers teams a consistent way to schedule, share and optimise GPU resources across clusters, whether on-prem or in the cloud.
In this blog, we will look at how Kubernetes can be used to orchestrate GPU workloads.
We will cover the basics of setting up clusters with GPU support, how to schedule and distribute workloads effectively, and strategies that help you get the most value from every GPU in your infrastructure.
Why Use Kubernetes for GPU Workloads?
Kubernetes provides a uniform way to deploy and manage applications, and this extends to GPU-accelerated workloads. Key benefits include:
Containerised GPU workloads can run in any environment with minimal modification. The NVIDIA GPU Operator helps abstract away platform-specific setup, making local and cloud deployment consistent.
Ease of Management
Rather than manually installing drivers and CUDA libraries on each node, Kubernetes supports automation via operators and Daemon Sets.
The NVIDIA GPU Operator installs all the necessary components to run the GPU. This simplifies GPU node setup significantly.
Scalability and Scheduling
Kubernetes can automatically scale GPU workloads across nodes by integrating with tools like the Cluster Autoscaler or Karpenter. These tools add or remove GPU enabled nodes based on workload demand.
Isolation and Multi-tenancy
By leveraging Kubernetes namespaces, RBAC, and resource quotas, teams can safely share GPU clusters. You can assign GPUs to specific teams and prevent overconsumption.
Unified Operations
If your organisation already runs other services on Kubernetes, extending existing clusters to include GPUs means single orchestration layer for all applications.
Operations teams can monitor and manage GPUs using the same tools and workflows they use for CPU-based services.
Kubernetes, combined with NVIDIA’s monitoring using DCGM exporter and node labelling, gives visibility into GPU utilization and health across the cluster
In short, Kubernetes provides a consistent, automated, and scalable way to deploy GPU accelerated applications, helping maximise the value of expensive GPU hardware while simplifying operational overheads.
NVIDIA GPU Operator
The NVIDIA GPU Operator is a convenient all-in-one solution that automates driver installation, device plugin deployment, and GPU node configuration. It manages all required NVIDIA software components, including:
- NVIDIA Drivers
- NVIDIA Container Toolkit
- Device plugins
- GPU Feature Discovery for automatic node labelling
- DCGM Exporter for GPU monitoring
With a single Helm chart deployment, GPU nodes become production ready across environments, whether bare metal or cloud.
Under the hood, the operator launches such as:
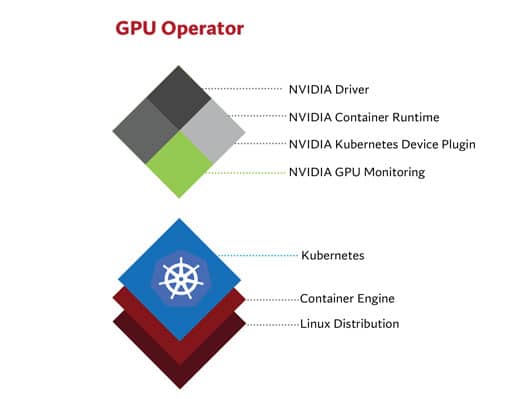
- nvidia-driver-daemonset (installs the driver kernel module)
- nvidia-device-plugin-daemonset (which registers GPUs)
- gpu-feature-discovery (which labels the node with GPU info)
After deployment, nodes expose labels such as:
nvidia.com/gpu.present=true
nvidia.com/gpu.count=1
nvidia.com/gpu.product=<GPU-Model>
This allows Kubernetes to schedule workloads correctly based on GPU availability.
Requesting a GPU in Kubernetes
Once GPU nodes are set up, requesting GPUs in workloads is simple. Here is a pod spec that asks for a single GPU:
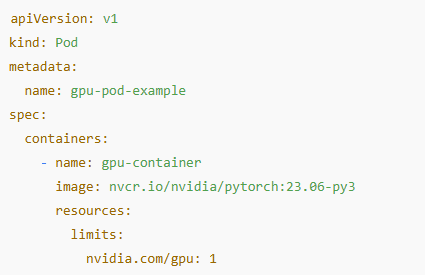
The limits field ensures Kubernetes schedules the pod on a GPU-capable node.
If no suitable nodes exist, the pod will stay pending until capacity frees up.
Common Challenges and Best Practices
Despite Kubernetes simplifying orchestration, several challenges still arise
- Resource fragmentation: workloads often underutilise GPU memory; NVIDIA MIG (Multi-instance GPU) allows partitioning of GPUs into logical instances with isolated compute and memory slices for better sharing.
- Scheduling constraints: jobs may get stuck if users request more GPUs than available; set resource quotas per namespace to prevent this
- Monitoring gaps: Kubernetes does not natively track GPU usage; integrate Prometheus + DCGM Exporter for detailed GPU metrics
Optimising for Cost and Efficiency
Given high cost of GPU, optimisation strategies are key:
- Right-size GPU types, use high-end GPUs for training, but cheaper (smaller) models for inference
- Partition GPUs with MIG for multiple smaller workloads
- Apply quotas to ensure fair usage across teams
- Autoscale GPU nodes with tools like Karpenter or Cluster Autoscaler
Key Takeaways
Kubernetes simplifies scaling, scheduling, and managing GPU workloads
The NVIDIA GPU Operator removes setup complexity
Cost and efficiency gains come from autoscaling, GPU partitioning (MIG), and smart scheduling
Future trends point toward more automation, cloud-native abstractions, and multi-accelerator support
Conclusion
GPUs are the engines behind today’s AI revolution. But without careful orchestration, they can have poor utilisation whether due to underuse, oversubscription, or inefficient workload scheduling.
This not only wastes valuable resources but also increases infrastructure costs. Kubernetes offers a clear path to unlocking its full potential by making GPU workloads easier to deploy, share and scale.
Whether you are just starting with GPU enabled nodes or already managing production scale AI workloads, combining Kubernetes with the NVIDIA GPU Operator gives you the tools to maximise performance and efficiency.
As the ecosystem evolves, Kubernetes is poised to be the unified platform for managing all AI hardware.

Muneeb Khan
Senior HPC Managed Service Specialist
Red Oak Consulting


